
Knee pain is a widespread symptom, signals stress in the body - the occurrence of a joint disease or simply increased leg load.
It is difficult to find a person who has never experienced pain in the knees in a certain lifetime.Complaints, clicks or pain of different intensities in the knee plates occur for many reasons in both adults and children.The older one person becomes, the higher the probability of different diseases, the first sign of pain in the knees.This can be attributed to the body's characteristics: Slowing metabolic processes, wearing the cartilage tissue of the joints, other problems with the musculoskeletal system, blood vessels, nerves.
Due to the complex anatomical structure, many structures and significant loads, and often overloads are very susceptible to the knee joints.The damage to each element of the structure, for example a synovial bag, leads to a violation of the motor function of the knee and the corresponding pain syndrome.Bands and Menisci are considered the most endangered, they are violated in 80–85% of cases.
The anatomical structure of the knee
The knee consists of a knee joint, a distal end of the thigh with two tumors and jackets, a tibia pipe bones, muscles, nerves, vessels, ligaments, a patella (knee chaste), joint bags and meniscus.
The knee joint is one of the large body connections.The thigh bone approaches him from above.The articular surfaces of its lateral (external) and medial (inner) condiles are articulated with the patella and the tibia.Meniski, the cartilage of the connective tissue, serves as a shock absorber of the joint.Thanks to them, a rational distribution of human weight occurs on a tiger plateau and the stability of the joint increases.Subtle, double-headed, half back and other muscles synchronize capsule league structures to ensure the motor activity of the knee joint.
The elements of the knee are connected by many ligaments.Within the connection there are two cross bands with crossed - front and front.The hobby bones are connected to the fiber and tibia bones with collateral tapes.The diagonal of the popliteal band is located in the back of the Bursa of the knee joint.The most important synovial capsule, which does not communicate with the joint, differs from a series of joint caves.The blood supply to the elements of the knee is carried out by a noble network of blood vessels, and the innervation is carried out by nerve fibers.
Causes of knee pain
There are many causes of the pain of the knee connections, which can be divided into several groups.
Traumatic lesions of the elements of the knee:
- Bitter knee.As a result of the blood gap, local bleeding occurs in the soft tissue of the joint.Reding, swelling, damage to the nerve end leads to pain, difficulties of movement.
- Full or partially band breaks.A partial violation of the integrity of the internal side volume, which results from an excessive twisting of the lower leg, is diagnosed more frequently.
The outer band breaks less often than the internal.This can be attributed to a strong deviation of the lowerbone inwards if the leg turns, for example.The break of the crossing bands is inevitably accompanied by hemarthrosis.
A complete break of both ligaments is often combined with damage to the common bag, which tears the inner meniscus.Such an injury leads to excessive mobility of the knee joint, accompanied by severe pain, the intensity of which depends on the degree of gap.
- Hemarthrosis of the knee joint - Pour blood into the articular cavity.There is a traumatic and non -human nature.Traumatic hemarthrosis is observed through meniscus fracture, complete or incomplete ligaments of ribbons, intra -articular fractures, bruising of the knee area.The non -human option is one of the symptoms of diseases characterized by an increased short form of the walls of blood vessels or a violation of the blood clotting system.This includes hemophilia, scurvy, severe forms of hemorrhagic diathesis.The blood that has accumulated in the joint cavity compresses the tissue and disturbs the bloodstream in them.A special pigment - hemosiderin - has a negative effect on the ligaments, hyaline cartilage, a synovial bag that leads to the loss of its elasticity.The result of the lesion of the common bource is the swelling of its villi and the increased production of articular fluid.The result of repeated bleeding is dystrophy and destruction of the joint.
- Knee meniscopathy - Violation of the integrity of the meniscus of the knee joint.In the lateral form, the outer meniscus with media inside is damaged.This is one of the most common, but difficult to diagnose damage to the knee joint.The risk zone of the disease is not only athletes who are involved in intensive training, but also ordinary people.The break of the meniscus can come from a sharp unusual movement when you turn your body, turn your leg, a strong blow onto your knee.
- Shifting of the knee switch - Patella pathological shift.The trauma is diagnosed in no more than 0.7% of cases. The total number of transfers is diagnosed.There is more often an external dislocation, less often - internally, very rarely - vertical or torsion.With an incomplete transfer, the knee switch is determined above the lateral (external) condyl with full outside of the lateral condyl.
- Closed or open fractures of the knee joint, the upper section of the bones of the lower leg or the lower spine. Such injuries are often combined with damage to the soft tissues of the knee, which causes massive bleeding, excessive mobility in the knee area, its deformation.
Inflammatory and degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the knee's joint elements:
- arthritis - Inflammatory damage to the knee joint.A similar mechanism for the development of pathology is observed in osteoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis and gout (with the deposition of urates in the joints).
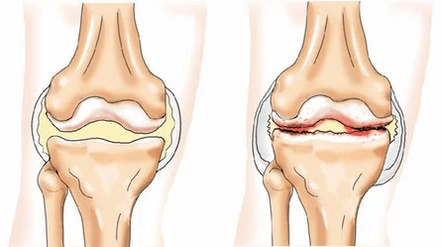
- Osteoarthrosis (gonarthrosis) With the defeat of the knee joint of non -inflammatory nature, which influences all of its structures and leads to serious degenerative changes.
- Bursitis With the inflammation of Synovial, Bursa leads to pain during bending and extending the movements in the knee.
- Periarthritis tendons of the knee joint - Inflammation of the capsule of the goose of the paws, the knee snails as well as the muscles and ligaments that surround the joint.In this case, the pain occurs mainly during the descent on the stairs, especially when the stress is severe, and focuses on the inner surface of the knee.
- Patella chondropathy -Degenerative non-chic changes in the cartilage of the articular (rear) surface of the patella.The degree of destruction can be different: from light areas that abrupt cracks soft and more complete.
- Chondromatosis - A serious chronic disease due to the dysplastic process with the island regeneration of the sections of the joint membrane in the cartilage chondrome.The ossification of individual cartilaginous body is not excluded.
- Baker cyst - The formation of a dense elastic round tumor formation in a popliteal fossa on the opposite side of the patella.The cyst is clearly visible in the exposed state of the knee.Causes discomfort, pain in the pop liteal region.In the case of significant sizes, it presses blood vessels and nerves, which leads to an impairment of innervation and blood circulation.
- Goff disease - An illness, accompanied by damage and further degeneration of adipose tissue that is around the knee joint.Press, edema and other damage to fat cells - adipocytes - end with their replacement through dense fiber fabric.As a result, the buffer function of the "fat pillow" is interrupted, the adipose tissue itself cannot be able to play the role of the shock absorber.
- Osgud -Switch disease - A pathology characterized by the murders of the faulty part of the Tibia.Diagnosis in young people from 10 to 18 years of playing sports.A painful bump appears under the absence of treatment under the patella, which leads to a restriction of the leg or complete immobilization as well as muscle hypotrophy.
Diseases in which radiation of pain in the knee is possible:
- Cokesart rose of the hip joint - Chronic damage to the hip joint, accompanied by progressive degeneration and dystrophic changes.The pain often spreads over the outer surface of the thigh onto the knee or below.
- Sedular nervous Europe - non -inflammatory damage to the nerve as a result of the compression squeeze or the spasming of blood vessels.This nerve reaches the feet, begins in the lower back and runs through the coccyx and the pelvis.The blockade at one point for your length leads to impaired sensitivity or pulsating pain.
- Fibromyalgia - Extraancing the defeat of soft tissues without anti -inflammatory nature with a combination of symptoms in the form of arthralgia, muscle weakness, depression, etc.
Some systemic diseases that lead to knee pain:
- osteoporosis - The disease of the bone system of a chronically progressive course that changes the mineral composition and the bone density."Washing" of calcium from bones leads to their fragility.The process is accompanied by smoke or painful pain in the limbs.
- Bone tuberculosis.The tubercular lesion of the bone site leads to constant severe pain.
- Osteomyelitis -an infectious and inflammatory disease that affects all structural elements of bones.The result of both specific, for example tuberculosis as well as not specific, frequent coccal osteomyelitis is a hyperemia of skin, edema, local acute pain in bones and muscles, Febrilt temperature.
- Some infectious diseases.In addition to the inclusion of the urogenital tract and the mucosa, the joints are affected by the rider syndrome.One of the manifestations of Lyme disease is arthralgia.
Types of knee pain
Depending on the etiology, nature and intensity of the pain can vary.
- Painful.With arthritis, osteoarthrosis.
- Acute, strong.With fractures of the knee elements, fracture of the ligaments, acute Buck -Through, the blue spots of the knee, a deterioration in meniscopathy and deforming osteoarthritis.
- Pulsating.With a deforming arthrosis, meniscus injury.
- Drill.With osteomyelitis.
- Dumb.With burit, chronic osteochondritis.
- combustion.With compression of the sciatic nerve, tuberculosis process in the bone.
- Burn. When pinching the nerve case.
- Pain when walking.With a bakery cyst, humpback fough, arthritis, gonarthrosis, periarthrid.
- The pain alone. With gout, arthritis.
Diagnosis of pathologies that cause knee pain
Physical examination:
- Collect anamnesis and complaints;
- Visual treatment with palpation of the knee.
Laboratory research:
- Biochemical and clinical blood tests;
- Serological blood test;
- Immunological blood test;
- rheumatological tests;
- Bacteriological analysis of the synovial fluid.
Invasive instrumental methods:
- Arthroscopy;
- Puncture of the common bag;
- Puncture biopsy.
Non -invasive instrumental diagnosis:
- Radiography of the knee joint;
- Densitometry;
- Ultrasound examination;
- MRI or CT.
Treatment of knee pain
If the pain in one or both knees of the non -human nature of the event, you should first contact the therapist who, due to the patient's symptoms and the results of an objective examination, leads to a narrow specialist - an orthopedist, a rheumatologist, a phlebologist or a neurologist.In the event of an injury, you have to contact a surgeon or an orthopedic trauma.
In any case, the treatment depends on the cause of the pain, ie on the type of injury or illness.Each disease has its own treatment scheme.But first the patient has to observe several general rules:
- Reduce the duration of hiking and stay on the legs considerably during the day;
- Athletes are temporarily (before recovery) training, and ordinary people from running or jumping;
- If you increase the pain, give up the movements completely, apply a fixing tape from an elastic bandage to the knee.
- Wear an association or an association to immobilize the knee joint;
- With a blue spot, cold instead of traumatic effects.
Rheumatoids, psoriasis arthritis, systemic autoimmune diseases require severe integrated treatment that has been carried out for many months.Basic therapy consists of immunosuppressors, non -steroidal inflammatory and hormonal medication, gold preparations, etc.
Pain relievers and anti -inflammatory drugs are used in the treatment of bursitis.If an infection is determined, then a course of antibiotics.The therapeutic puncture of the bag is carried out to remove excess liquid from the synovial cavity and/or the introduction of one of its corticosteroids.The operation helps to eliminate the chronic inflammation of the brush - the surgical excision of the synovial bag.
With deforming osteoarthritis, intra -karticular injections of glucocorticosteroids, an extended absorption of NSAIDS and chondroprotectors are effective.In order to relieve pain syndrome, compresses with dimexid or bishop, ointments and gels are prescribed locally with anti -inflammatory effects.Massage, physiotherapy, therapeutic gymnastics helps.Heavy lesions of the knee joint require surgical intervention - joint endoprosthetics.
The treatment of osteoporosis exists in the course of taking bisphosphonates, calcium preparations, vitamin D etc.
Treatment of the meniscal break can be conservative or surgical.Conservative therapy consists of analgesics, NSAIDs, hyaluronic acid and chondroprotectors.But first the common reduction is carried out.
Types of surgical interventions:
- Menisectomy;
- partial (incomplete) menisectomy;
- Meniscal plant;
- Arthroscopy;
- Arthroscopic seams of the break of the meniscus.
With every violation of the knee, the rehabilitation phase is after the treatment, which should take place under the control of a rehabilitologist or orthopedic surgeon under the control of a rehabilitologist.The doctor will create an optimal joint recovery program.The main methods of postoperative rehabilitation are massage and therapeutic gymnastics.Classes for special simulators are also effective and gradually develop a knee joint.




















